FalconSAT-3 was built in 2005 and 2006 by cadets and faculty in the Space Systems Research Center at the US Air Force Academy in Colorado Springs, CO.
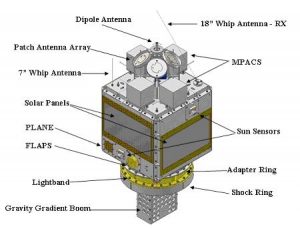
In amateur service the downlink is at 435.103 MHz transmitting 1W into a ¼ whip that extends from a corner of the satellite near the Lightband separation ring. The uplink is at 145.840 MHz and the receive antenna is a ¼ whip on the opposite side of the satellite near the S-band antennas. All UHF and S-band equipment on NTIA licensed frequencies has been disabled. The ARS VHF receiver is very sensitive. Modulation is 9600 bps GMSK for the uplink and downlink. The broadcast callsign is PFS3-11, and the BBS callsign is PFS3-12, Unproto APRS via PFS3-1.
The core avionics were designed and built Mark, N4TPY, and Dino, KC4YMG at SpaceQuest and have performed remarkably well for 10 years on orbit. Jim, WD0E, was the lead engineer for FalconSAT-3 at the AFA and managed the design, construction, testing and early operations of the satellite. Inquiries about current operations should be directed to AMSAT VP Operations Drew Glasbrenner, KO4MA (ko4ma@amsat.org)
Amsat Falconsat 3 page
