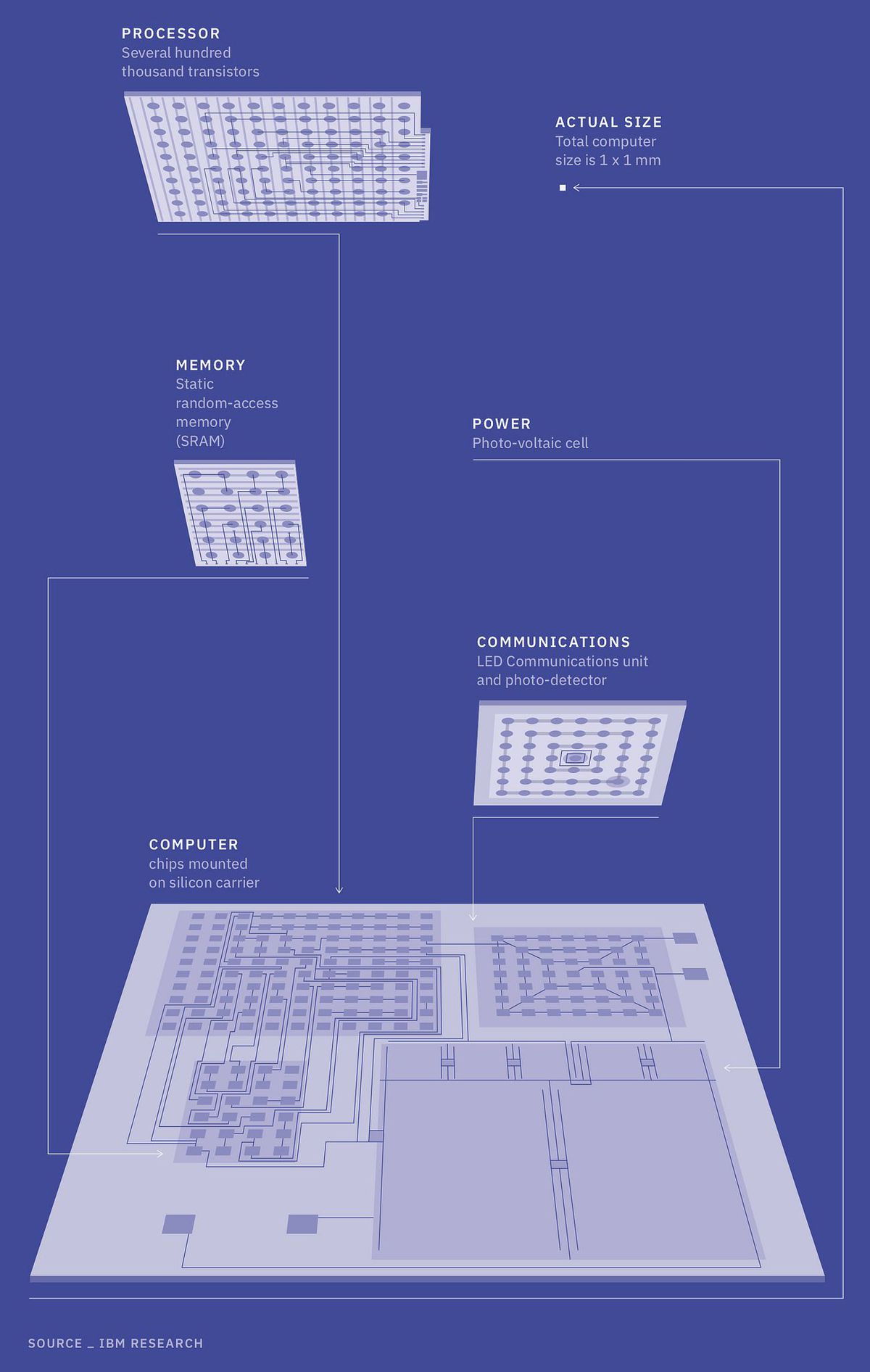
March 19 is the first day of IBM Think 2018, the company’s flagship conference, where the company will unveil what it claims is the world’s smallest computer. They’re not kidding: It’s literally smaller than a grain of salt.
But don’t let the size fool you: This sucker has the computing power of the x86 chip from 1990. Okay, so that’s not great compared to what we have today, but cut it some slack — you need a microscope to see it.
The computer will cost less than ten cents to manufacture, and will also pack “several hundred thousand transistors,” according to the company. These will allow it to “monitor, analyze, communicate, and even act on data.”
[…]
According to IBM, this is only the beginning. “Within the next five years, cryptographic anchors — such as ink dots or tiny computers smaller than a grain of salt — will be embedded in everyday objects and devices,” says IBM head of research Arvind Krishna. If he’s correct, we’ll see way more of these tiny systems in objects and devices in the years to come.
Source: IBM unveils ‘world’s smallest computer’ with blockchain at Think 2018