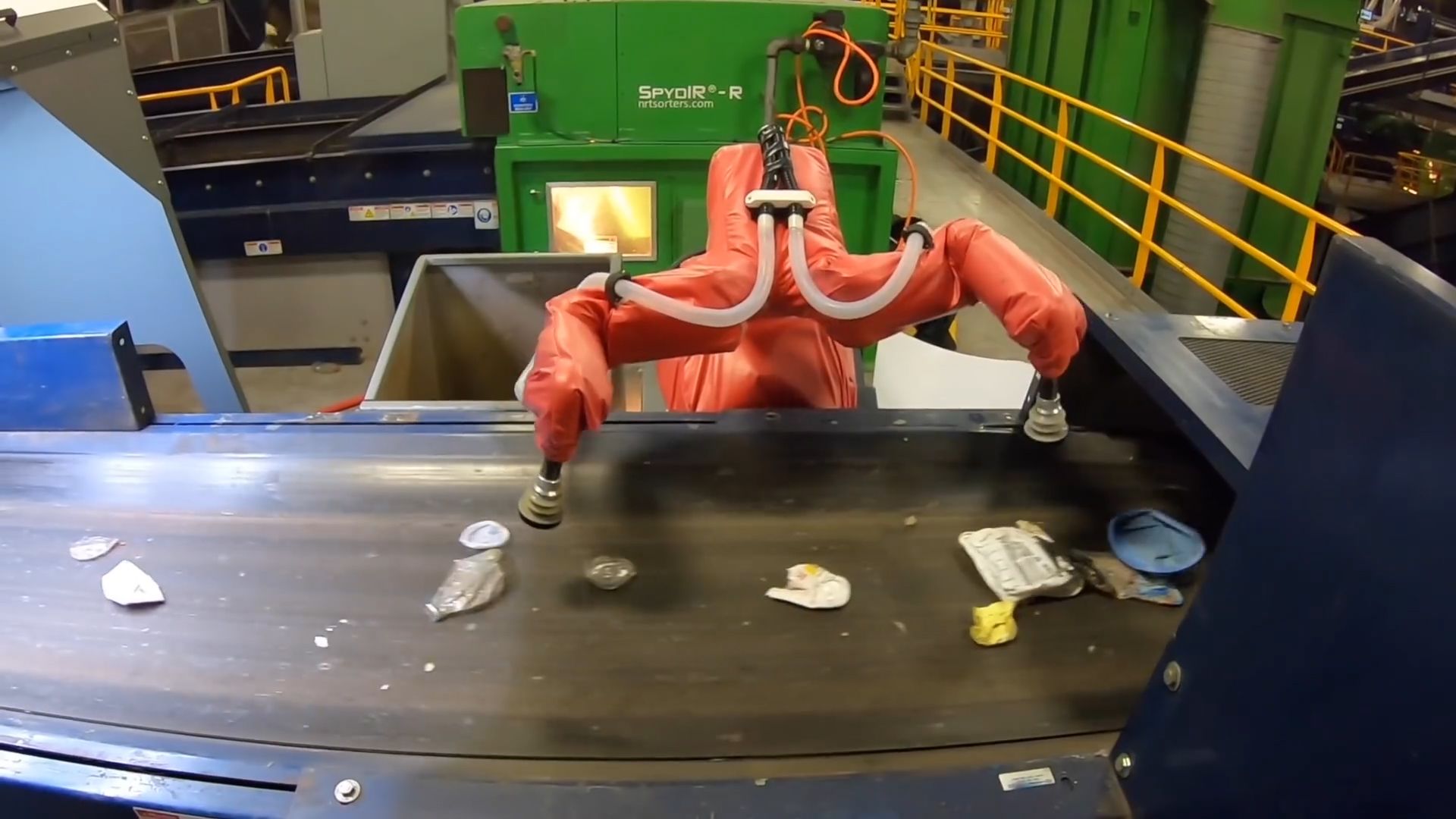
The way the robots work is simple. Guided by cameras and computer systems trained to recognize specific objects, the robots’ arms glide over moving conveyor belts until they reach their target. Oversized tongs or fingers with sensors that are attached to the arms snag cans, glass, plastic containers, and other recyclable items out of the rubbish and place them into nearby bins.
The robots — most of which have come online only within the past year — are assisting human workers and can work up to twice as fast. With continued improvements in the bots’ ability to spot and extract specific objects, they could become a formidable new force in the $6.6 billion U.S. industry.
Researchers like Lily Chin, a PhD. student at the Distributed Robotics Lab at MIT, are working to develop sensors for these robots that can improve their tactile capabilities and improve their sense of touch so they can determine plastic, paper and metal through their fingers. “Right now, robots are mostly reliant on computer vision, but they can get confused and make mistakes,” says Chin. “So now we want to integrate these new tactile capabilities.”
Denver-based AMP Robotics, is one of the companies on the leading edge of innovation in the field. It has developed software — a AMP Neuron platform that uses computer vision and machine learning — so robots can recognize different colors, textures, shapes, sizes and patterns to identify material characteristics so they can sort waste.
The robots are being installed at the Single Stream Recyclers plant in Sarasota, Florida and they will be able to pick 70 to 80 items a minute, twice as fast as humanly possible and with greater accuracy.
Bulk Handling Systems Max-AI AQC-C robotBulk Handling Systems“Using this technology you can increase the quality of the material and in some cases double or triple its resale value,” says AMP Robotics CEO Mantaya Horowitz. “Quality standards are getting stricter that’s why companies and researchers are working on high tech solutions.”
Source: Meet the robots being used to help solve America’s recycling crisis