Every minute of every day, everywhere on the planet, dozens of companies — largely unregulated, little scrutinized — are logging the movements of tens of millions of people with mobile phones and storing the information in gigantic data files. The Times Privacy Project obtained one such file, by far the largest and most sensitive ever to be reviewed by journalists. It holds more than 50 billion location pings from the phones of more than 12 million Americans as they moved through several major cities, including Washington, New York, San Francisco and Los Angeles.
Each piece of information in this file represents the precise location of a single smartphone over a period of several months in 2016 and 2017. The data was provided to Times Opinion by sources who asked to remain anonymous because they were not authorized to share it and could face severe penalties for doing so. The sources of the information said they had grown alarmed about how it might be abused and urgently wanted to inform the public and lawmakers.
[Related: How to Track President Trump — Read more about the national security risks found in the data.]
After spending months sifting through the data, tracking the movements of people across the country and speaking with dozens of data companies, technologists, lawyers and academics who study this field, we feel the same sense of alarm. In the cities that the data file covers, it tracks people from nearly every neighborhood and block, whether they live in mobile homes in Alexandria, Va., or luxury towers in Manhattan.
One search turned up more than a dozen people visiting the Playboy Mansion, some overnight. Without much effort we spotted visitors to the estates of Johnny Depp, Tiger Woods and Arnold Schwarzenegger, connecting the devices’ owners to the residences indefinitely.
If you lived in one of the cities the dataset covers and use apps that share your location — anything from weather apps to local news apps to coupon savers — you could be in there, too.
If you could see the full trove, you might never use your phone the same way again.
A typical day at Grand Central Terminal
in New York City
Satellite imagery: Microsoft
The data reviewed by Times Opinion didn’t come from a telecom or giant tech company, nor did it come from a governmental surveillance operation. It originated from a location data company, one of dozens quietly collecting precise movements using software slipped onto mobile phone apps. You’ve probably never heard of most of the companies — and yet to anyone who has access to this data, your life is an open book. They can see the places you go every moment of the day, whom you meet with or spend the night with, where you pray, whether you visit a methadone clinic, a psychiatrist’s office or a massage parlor.
[…]
The companies that collect all this information on your movements justify their business on the basis of three claims: People consent to be tracked, the data is anonymous and the data is secure.
None of those claims hold up, based on the file we’ve obtained and our review of company practices.
Yes, the location data contains billions of data points with no identifiable information like names or email addresses. But it’s child’s play to connect real names to the dots that appear on the maps.
[…]
In most cases, ascertaining a home location and an office location was enough to identify a person. Consider your daily commute: Would any other smartphone travel directly between your house and your office every day?
Describing location data as anonymous is “a completely false claim” that has been debunked in multiple studies, Paul Ohm, a law professor and privacy researcher at the Georgetown University Law Center, told us. “Really precise, longitudinal geolocation information is absolutely impossible to anonymize.”
“D.N.A.,” he added, “is probably the only thing that’s harder to anonymize than precise geolocation information.”
[Work in the location tracking industry? Seen an abuse of data? We want to hear from you. Using a non-work phone or computer, contact us on a secure line at 440-295-5934, @charliewarzel on Wire or email Charlie Warzel and Stuart A. Thompson directly.]
Yet companies continue to claim that the data are anonymous. In marketing materials and at trade conferences, anonymity is a major selling point — key to allaying concerns over such invasive monitoring.
To evaluate the companies’ claims, we turned most of our attention to identifying people in positions of power. With the help of publicly available information, like home addresses, we easily identified and then tracked scores of notables. We followed military officials with security clearances as they drove home at night. We tracked law enforcement officers as they took their kids to school. We watched high-powered lawyers (and their guests) as they traveled from private jets to vacation properties. We did not name any of the people we identified without their permission.
The data set is large enough that it surely points to scandal and crime but our purpose wasn’t to dig up dirt. We wanted to document the risk of underregulated surveillance.
Watching dots move across a map sometimes revealed hints of faltering marriages, evidence of drug addiction, records of visits to psychological facilities.
Connecting a sanitized ping to an actual human in time and place could feel like reading someone else’s diary.
[…]
The inauguration weekend yielded a trove of personal stories and experiences: elite attendees at presidential ceremonies, religious observers at church services, supporters assembling across the National Mall — all surveilled and recorded permanently in rigorous detail.
Protesters were tracked just as rigorously. After the pings of Trump supporters, basking in victory, vanished from the National Mall on Friday evening, they were replaced hours later by those of participants in the Women’s March, as a crowd of nearly half a million descended on the capital. Examining just a photo from the event, you might be hard-pressed to tie a face to a name. But in our data, pings at the protest connected to clear trails through the data, documenting the lives of protesters in the months before and after the protest, including where they lived and worked.
[…]
Inauguration Day weekend was marked by other protests — and riots. Hundreds of protesters, some in black hoods and masks, gathered north of the National Mall that Friday, eventually setting fire to a limousine near Franklin Square. The data documented those rioters, too. Filtering the data to that precise time and location led us to the doorsteps of some who were there. Police were present as well, many with faces obscured by riot gear. The data led us to the homes of at least two police officers who had been at the scene.
As revealing as our searches of Washington were, we were relying on just one slice of data, sourced from one company, focused on one city, covering less than one year. Location data companies collect orders of magnitude more information every day than the totality of what Times Opinion received.
Data firms also typically draw on other sources of information that we didn’t use. We lacked the mobile advertising IDs or other identifiers that advertisers often combine with demographic information like home ZIP codes, age, gender, even phone numbers and emails to create detailed audience profiles used in targeted advertising. When datasets are combined, privacy risks can be amplified. Whatever protections existed in the location dataset can crumble with the addition of only one or two other sources.
There are dozens of companies profiting off such data daily across the world — by collecting it directly from smartphones, creating new technology to better capture the data or creating audience profiles for targeted advertising.
The full collection of companies can feel dizzying, as it’s constantly changing and seems impossible to pin down. Many use technical and nuanced language that may be confusing to average smartphone users.
While many of them have been involved in the business of tracking us for years, the companies themselves are unfamiliar to most Americans. (Companies can work with data derived from GPS sensors, Bluetooth beacons and other sources. Not all companies in the location data business collect, buy, sell or work with granular location data.)

A Selection of Companies Working
in the Location Data Business
Sources: MightySignal, LUMA Partners and AppFigures.
Location data companies generally downplay the risks of collecting such revealing information at scale. Many also say they’re not very concerned about potential regulation or software updates that could make it more difficult to collect location data.
[…]
Does it really matter that your information isn’t actually anonymous? Location data companies argue that your data is safe — that it poses no real risk because it’s stored on guarded servers. This assurance has been undermined by the parade of publicly reported data breaches — to say nothing of breaches that don’t make headlines. In truth, sensitive information can be easily transferred or leaked, as evidenced by this very story.
We’re constantly shedding data, for example, by surfing the internet or making credit card purchases. But location data is different. Our precise locations are used fleetingly in the moment for a targeted ad or notification, but then repurposed indefinitely for much more profitable ends, like tying your purchases to billboard ads you drove past on the freeway. Many apps that use your location, like weather services, work perfectly well without your precise location — but collecting your location feeds a lucrative secondary business of analyzing, licensing and transferring that information to third parties.
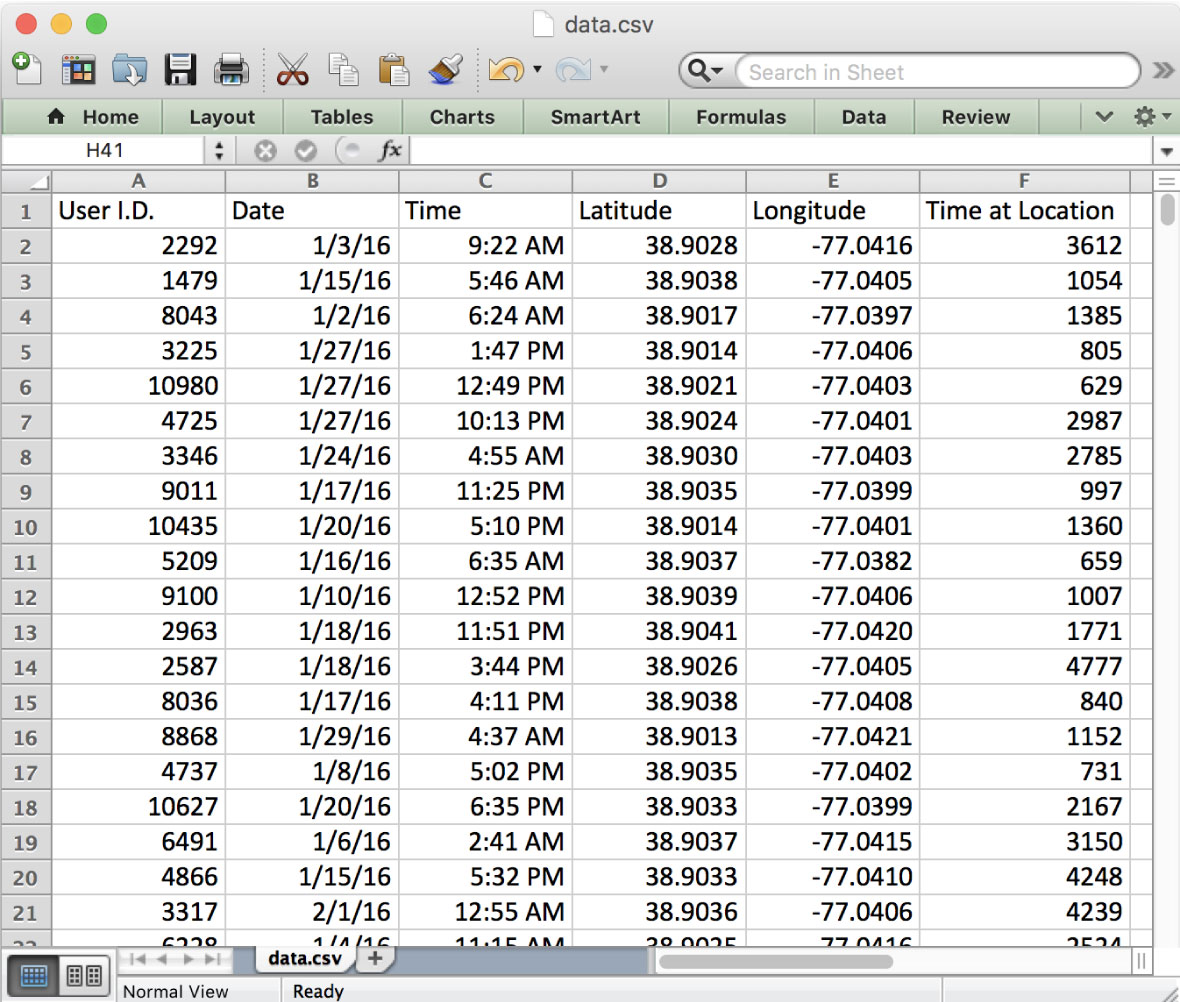
The data contains simple information like date, latitude and longitude, making it easy to inspect, download and transfer. Note: Values are randomized to protect sources and device owners.
For many Americans, the only real risk they face from having their information exposed would be embarrassment or inconvenience. But for others, like survivors of abuse, the risks could be substantial. And who can say what practices or relationships any given individual might want to keep private, to withhold from friends, family, employers or the government? We found hundreds of pings in mosques and churches, abortion clinics, queer spaces and other sensitive areas.
In one case, we observed a change in the regular movements of a Microsoft engineer. He made a visit one Tuesday afternoon to the main Seattle campus of a Microsoft competitor, Amazon. The following month, he started a new job at Amazon. It took minutes to identify him as Ben Broili, a manager now for Amazon Prime Air, a drone delivery service.
“I can’t say I’m surprised,” Mr. Broili told us in early December. “But knowing that you all can get ahold of it and comb through and place me to see where I work and live — that’s weird.” That we could so easily discern that Mr. Broili was out on a job interview raises some obvious questions, like: Could the internal location surveillance of executives and employees become standard corporate practice?
[…]
If this kind of location data makes it easy to keep tabs on employees, it makes it just as simple to stalk celebrities. Their private conduct — even in the dead of night, in residences and far from paparazzi — could come under even closer scrutiny.
Reporters hoping to evade other forms of surveillance by meeting in person with a source might want to rethink that practice. Every major newsroom covered by the data contained dozens of pings; we easily traced one Washington Post journalist through Arlington, Va.
In other cases, there were detours to hotels and late-night visits to the homes of prominent people. One person, plucked from the data in Los Angeles nearly at random, was found traveling to and from roadside motels multiple times, for visits of only a few hours each time.
While these pointillist pings don’t in themselves reveal a complete picture, a lot can be gleaned by examining the date, time and length of time at each point.
Large data companies like Foursquare — perhaps the most familiar name in the location data business — say they don’t sell detailed location data like the kind reviewed for this story but rather use it to inform analysis, such as measuring whether you entered a store after seeing an ad on your mobile phone.
But a number of companies do sell the detailed data. Buyers are typically data brokers and advertising companies. But some of them have little to do with consumer advertising, including financial institutions, geospatial analysis companies and real estate investment firms that can process and analyze such large quantities of information. They might pay more than $1 million for a tranche of data, according to a former location data company employee who agreed to speak anonymously.
Location data is also collected and shared alongside a mobile advertising ID, a supposedly anonymous identifier about 30 digits long that allows advertisers and other businesses to tie activity together across apps. The ID is also used to combine location trails with other information like your name, home address, email, phone number or even an identifier tied to your Wi-Fi network.
The data can change hands in almost real time, so fast that your location could be transferred from your smartphone to the app’s servers and exported to third parties in milliseconds. This is how, for example, you might see an ad for a new car some time after walking through a dealership.
That data can then be resold, copied, pirated and abused. There’s no way you can ever retrieve it.
Location data is about far more than consumers seeing a few more relevant ads. This information provides critical intelligence for big businesses. The Weather Channel app’s parent company, for example, analyzed users’ location data for hedge funds, according to a lawsuit filed in Los Angeles this year that was triggered by Times reporting. And Foursquare received much attention in 2016 after using its data trove to predict that after an E. coli crisis, Chipotle’s sales would drop by 30 percent in the coming months. Its same-store sales ultimately fell 29.7 percent.
Much of the concern over location data has focused on telecom giants like Verizon and AT&T, which have been selling location data to third parties for years. Last year, Motherboard, Vice’s technology website, found that once the data was sold, it was being shared to help bounty hunters find specific cellphones in real time. The resulting scandal forced the telecom giants to pledge they would stop selling location movements to data brokers.
Yet no law prohibits them from doing so.
[…]
If this information is so sensitive, why is it collected in the first place?
For brands, following someone’s precise movements is key to understanding the “customer journey” — every step of the process from seeing an ad to buying a product. It’s the Holy Grail of advertising, one marketer said, the complete picture that connects all of our interests and online activity with our real-world actions.
Once they have the complete customer journey, companies know a lot about what we want, what we buy and what made us buy it. Other groups have begun to find ways to use it too. Political campaigns could analyze the interests and demographics of rally attendees and use that information to shape their messages to try to manipulate particular groups. Governments around the world could have a new tool to identify protestors.
Pointillist location data also has some clear benefits to society. Researchers can use the raw data to provide key insights for transportation studies and government planners. The City Council of Portland, Ore., unanimously approved a deal to study traffic and transit by monitoring millions of cellphones. Unicef announced a plan to use aggregated mobile location data to study epidemics, natural disasters and demographics.
For individual consumers, the value of constant tracking is less tangible. And the lack of transparency from the advertising and tech industries raises still more concerns.
Does a coupon app need to sell second-by-second location data to other companies to be profitable? Does that really justify allowing companies to track millions and potentially expose our private lives?
Data companies say users consent to tracking when they agree to share their location. But those consent screens rarely make clear how the data is being packaged and sold. If companies were clearer about what they were doing with the data, would anyone agree to share it?
What about data collected years ago, before hacks and leaks made privacy a forefront issue? Should it still be used, or should it be deleted for good?
If it’s possible that data stored securely today can easily be hacked, leaked or stolen, is this kind of data worth that risk?
Is all of this surveillance and risk worth it merely so that we can be served slightly more relevant ads? Or so that hedge fund managers can get richer?
The companies profiting from our every move can’t be expected to voluntarily limit their practices. Congress has to step in to protect Americans’ needs as consumers and rights as citizens.
Until then, one thing is certain: We are living in the world’s most advanced surveillance system. This system wasn’t created deliberately. It was built through the interplay of technological advance and the profit motive. It was built to make money. The greatest trick technology companies ever played was persuading society to surveil itself.