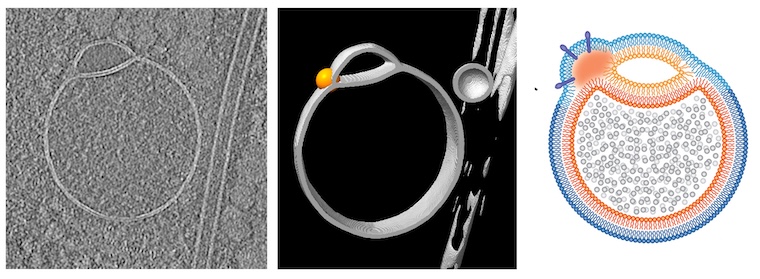
A groundbreaking study from the University of Auckland and Chalmers University of Technology is offering new hope for spinal cord injury patients. Researchers have developed an ultra-thin implant that delivers gentle electric currents directly to the injured spinal cord. This device mimics natural developmental signals to stimulate nerve healing, and in animal trials, it restored movement and touch sensation in rats—without causing inflammation or damage.
[…]
Spinal cord injuries shatter the signal between the brain and body, often resulting in a loss of function.”Unlike a cut on the skin, which typically heals on its own, the spinal cord does not regenerate effectively, making these injuries devastating and currently incurable,”
[…]
“We developed an ultra-thin implant designed to sit directly on the spinal cord, precisely positioned over the injury site in rats,” Dr Harland says.
The device delivers a carefully controlled electrical current across the injury site. “The aim is to stimulate healing so people can recover functions lost through spinal-cord injury,” Professor Darren Svirskis, director of the CatWalk Cure Program at the University’s School of Pharmacy says.
[…]
After four weeks, animals that received daily electric field treatment showed improved movement compared with those who did not.
Throughout the 12-week study, they responded more quickly to gentle touch.
“This indicates that the treatment supported recovery of both movement and sensation,” Harland says. “Just as importantly, our analysis confirmed that the treatment did not cause inflammation or other damage to the spinal cord, demonstrating that it was not only effective but also safe.”
[…]
Source: A tiny implant just helped paralyzed rats walk again—is human recovery next? | ScienceDaily