[…]
when politicians are demanding that technologists NERD HARDER! to realize their cherished impossibilities.
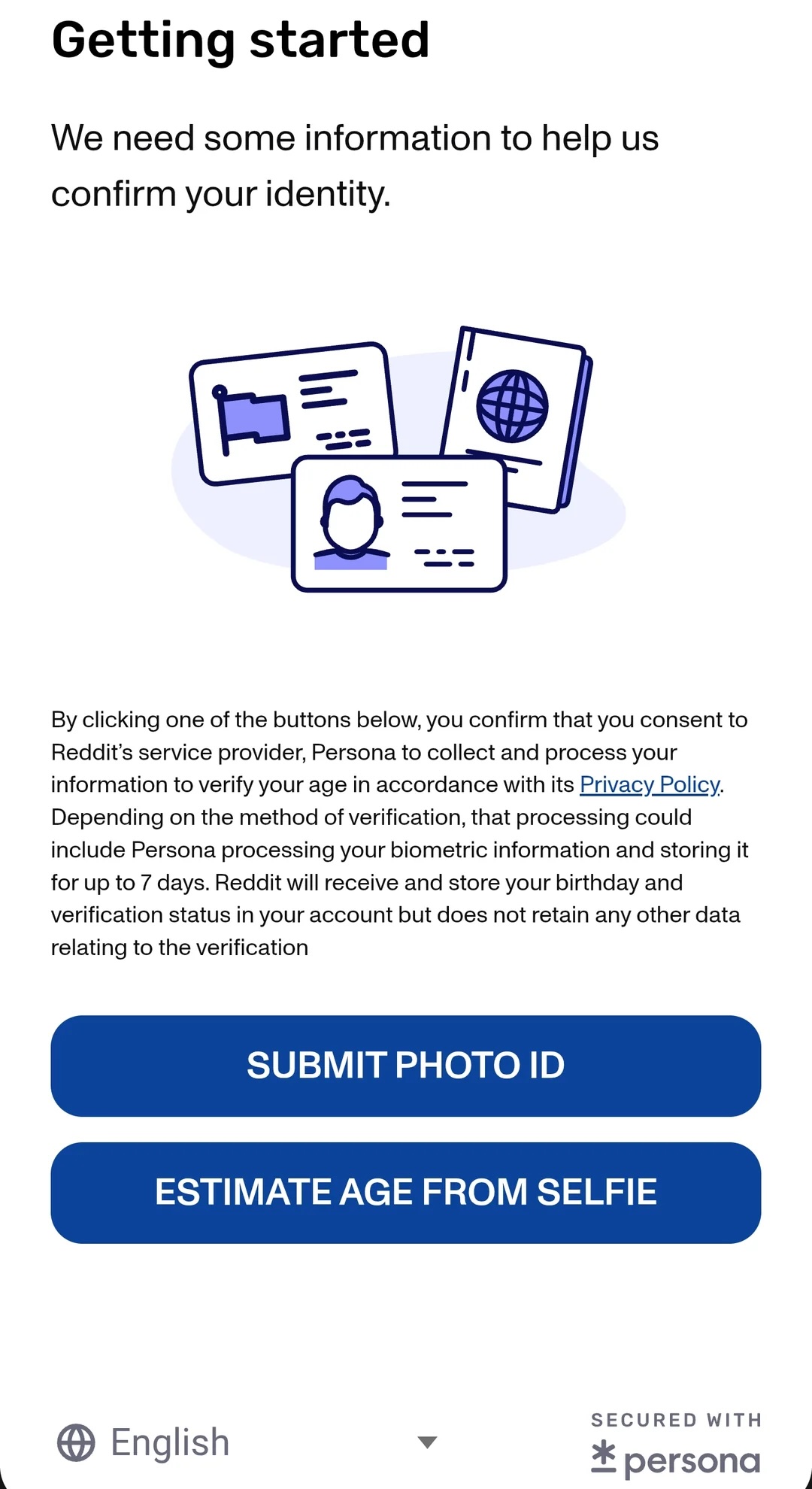
That’s just happened, and in relation to one of the scariest, most destructive NERD HARDER! tech policies ever to be assayed (a stiff competition). I’m talking about the UK Online Safety Act, which imposes a duty on websites to verify the age of people they communicate with before serving them anything that could be construed as child-inappropriate (a category that includes, e.g., much of Wikipedia):
https://wikimediafoundation.org/news/2025/08/11/wikimedia-foundation-challenges-uk-online-safety-act-regulations/
The Starmer government has, incredibly, developed a passion for internet regulations that are even stupider than Tony Blair’s and David Cameron’s. Requiring people to identify themselves (generally, via their credit cards) in order to look at porn will create a giant database of every kink and fetish of every person in the UK, which will inevitably leak and provide criminals and foreign spies with a kompromat system they can sort by net worth of the people contained within.
This hasn’t deterred Starmer, who insists that if we just NERD HARDER!, we can use things like “zero-knowledge proofs” to create “privacy-preserving” age verification system, whereby a service can assure itself that it is communicating with an adult without ever being able to determine who it is communicating with.
In support of this idea, Starmer and co like to cite some genuinely exciting and cool cryptographic work on privacy-preserving credential schemes. Now, one of the principal authors of the key papers on these credential schemes, Steve Bellovin, has published a paper that is pithily summed up via its title, “Privacy-Preserving Age Verification—and Its Limitations”:
https://www.cs.columbia.edu/~smb/papers/age-verify.pdf
The tldr of this paper is that Starmer’s idea will not work and cannot work. The research he relies on to defend the technological feasibility of his cherished plan does not support his conclusion.
Bellovin starts off by looking at the different approaches various players have mooted for verifying their users’ age. For example, Google says it can deploy a “behavioral” system that relies on Google surveillance dossiers to make guesses about your age. Google refuses to explain how this would work, but Bellovin sums up several of the well-understood behavioral age estimation techniques and explains why they won’t work. It’s one thing to screw up age estimation when deciding which ad to show you; it’s another thing altogether to do this when deciding whether you can access the internet.
Others say they can estimate your age by using AI to analyze a picture of your face. This is a stupid idea for many reasons, not least of which is that biometric age estimation is notoriously unreliable when it comes to distinguishing, say, 16 or 17 year olds from 18 year olds. Nevertheless, there are sitting US Congressmen who not only think this would work – they labor under the misapprehension that this is already going on:
https://pluralistic.net/2023/04/09/how-to-make-a-child-safe-tiktok/
So that just leaves the privacy-preserving credential schemes, especially the Camenisch-Lysyanskaya protocol. This involves an Identity Provider (IDP) that establishes a user’s identity and characteristics using careful document checks and other procedures. The IDP then hands the user a “primary credential” that can attest to everything the IDP knows about the user, and any number of “subcredentials” that only attest to specific facts about that user (such as their age).
These are used in zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) – a way for two parties to validate that one of them asserts a fact without learning what that fact is in the process (this is super cool stuff). Users can send their subcredentials to a third party, who can use a ZKP to validate them without learning anything else about the user – so you could prove your age (or even just prove that you are over 18 without disclosing your age at all) without disclosing your identity.
There’s some good news for implementing CL on the web: rather than developing a transcendentally expensive and complex new system for these credential exchanges and checks, CL can piggyback on the existing Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) that powers your browser’s ability to have secure sessions when you visit a website with https:// in front of the address (instead of just http://).
However, doing so poses several difficulties, which Bellovin enumerates under a usefully frank section header: “INSURMOUNTABLE OBSTACLES.”
The most insurmountable of these obstacles is getting set up with an IDP in the first place – that is, proving who you are to some agency, but only one such agency (so you can’t create two primary credentials and share one of them with someone underage). Bellovin cites Supreme Court cases about voter ID laws and the burdens they impose on people who are poor, old, young, disabled, rural, etc.
Fundamentally, it can be insurmountably hard for a lot of people to get, say, a driver’s license, or any other singular piece of ID that they can provide to an IDP in order to get set up on the system.
The usual answer for this is for IDPs to allow multiple kinds of ID. This does ease the burden on users, but at the expense of creating fatal weaknesses in the system: if you can set up an identity with multiple kinds of ID, you can visit different IDPs and set up an ID with each (just as many Americans today have drivers licenses from more than one state).
The next obstacle is “user challenges,” like the problem of households with shared computers, or computers in libraries, hotels, community centers and other public places. The only effective way to do this is to create (expensive) online credential stores, which are likely to be out of reach of the poor and disadvantaged people who disproportionately rely on public or shared computers.
Next are the “economic issues”: this stuff is expensive to set up and maintain, and someone’s gotta pay for it. We could ask websites that offer kid-inappropriate content to pay for it, but that sets up an irreconcilable conflict of interest. These websites are going to want to minimize their costs, and everything they can do to reduce costs will make the system unacceptably worse. For example, they could choose only to set up accounts with IDPs that are local to the company that operates the server, meaning that anyone who lives somewhere else and wants to access that website is going to have to somehow get certified copies of e.g. their birth certificate and driver’s license to IDPs on the other side of the planet. The alternative to having websites foot the bill for this is asking users to pay for it – meaning that, once again, we exclude poor people from the internet.
Finally, there’s “governance”: who runs this thing? In practice, the security and privacy guarantees of the CL protocol require two different kinds of wholly independent institutions: identity providers (who verify your documents), and certificate authorities (who issue cryptographic certificates based on those documents). If these two functions take place under one roof, the privacy guarantees of the system immediately evaporate.
An IDP’s most important role is verifying documents and associating them with a specific person. But not all IDPs will be created equal, and people who wish to cheat the system will gravitate to the worst IDPs. However, lots of people who have no nefarious intent will also use these IDPs, merely because they are close by, or popular, or were selected at random. A decision to strike off an IDP and rescind its verifications will force lots of people – potentially millions of people – to start over with the whole business of identifying themselves, during which time they will be unable to access much of the web. There’s no practical way for the average person to judge whether an IDP they choose is likely to be found wanting in the future.
So we can regulate IDPs, but who will do the regulation? Age verification laws affect people outside of a government’s national territory – anyone seeking to access content on a webserver falls under age verification’s remit. Remember, IDPs handle all kinds of sensitive data: do you want Russia, say, to have a say in deciding who can be an IDP and what disclosure rules you will have to follow?
To regulate IDPs (and certificate authorities), these entities will have to keep logs, which further compromises the privacy guarantees of the CL protocol.
Looming all of this is a problem with the CL protocol as being built on regulated entities, which is that CL is envisioned as a way to do all kinds of business, from opening a bank account to proving your vaccination status or your right to work or receive welfare. Authoritarian governments who order primary credential revocations of their political opponents could thoroughly and terrifyingly “unperson” them at the stroke of a pen.
The paper’s conclusions provide a highly readable summary of these issues, which constitute a stinging rebuke to anyone contemplating age-verification schemes. These go well beyond the UK, and are in the works in Canada, Australia, the EU, Texas and Louisiana.
Age verification is an impossibility, and an impossibly terrible idea with impossibly vast consequences for privacy and the open web, as my EFF colleague Jason Kelley explained on the Malwarebytes podcast:
https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/podcast/2025/08/the-worst-thing-for-online-rights-an-age-restricted-grey-web-lock-and-code-s06e16
Politicians – even nontechnical ones – can make good tech policy, provided they take expert feedback seriously (and distinguish it from self-interested industry lobbying).
When it comes to tech policy, wanting it badly is not enough. The fact that it would be really cool if we could get technology to do something has no bearing on whether we can actually get technology to do that thing. NERD HARDER! isn’t a policy, it’s a wish.
Wish in one hand and shit in the other and see which one will be full first:
https://www.reddit.com/r/etymology/comments/oqiic7/studying_the_origins_of_the_phrase_wish_in_one/