A team of researchers has demonstrated for the first time a single-molecule electret – a device that could be one of the keys to molecular computers.
Smaller electronics are crucial to developing more advanced computers and other devices. This has led to a push in the field toward finding a way to replace silicon chips with molecules, an effort that includes creating single-molecule electret – a switching device that could serve as a platform for extremely small non-volatile storage devices. Because it seemed that such a device would be so unstable, however, many in the field wondered whether one could ever exist.
Along with colleagues at Nanjing University, Renmin University, Xiamen University, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Mark Reed, the Harold Hodgkinson Professor of Electrical Engineering & Applied Physics demonstrated a single-molecule electret with a functional memory. The results were published Oct. 12 in Nature Nanotechnology.
Most electrets are made of piezoelectric materials, such as those that produce the sound in speakers. In an electret, all the dipoles – pairs of opposite electric charges – spontaneously line up in the same direction. By applying an electric field, their directions can be reversed.
“The question has always been about how small you could make these electrets, which are essentially memory storage devices,” Reed said.
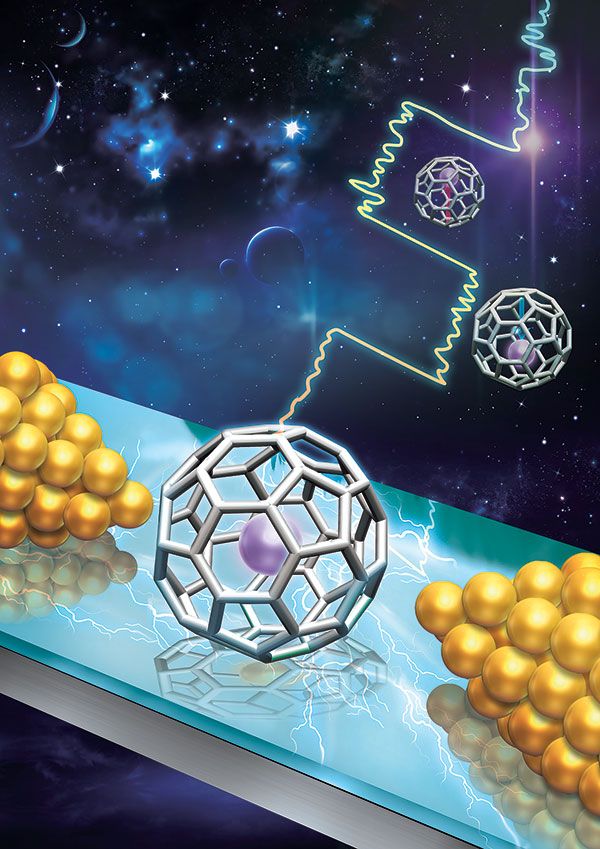
The researchers inserted an atom of Gadolinium (Gd) inside a carbon buckyball, a 32-sided molecule, also known as a buckminsterfullerene. When the researchers put this construct (Gd@C82) in a transistor-type structure, they observed single electron transport and used this to understand its energy states. However, the real breakthrough was that they discovered that they could use an electric field to switch its energy state from one stable state to another.
“What’s happening is that this molecule is acting as if it has two stable polarization states,” Reed said. He added that the team ran a variety of experiments, measuring the transport characteristics while applying an electric field, and switching the states back and forth. “We showed that we could make a memory of it – read, write, read, write,” he said.
Reed emphasized that the present device structure isn’t currently practical for any application, but proves that the underlying science behind it is possible.
“The important thing in this is that it shows you can create in a molecule two states that cause the spontaneous polarization and two switchable states,” he said. “And this can give people ideas that maybe you can shrink memory down literally to the single molecular level. Now that we understand that we can do that, we can move on to do more interesting things with it.”

 Along with colleagues at Nanjing University, Renmin University, Xiamen University, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Mark Reed, the Harold Hodgkinson Professor of Electrical Engineering & Applied Physics demonstrated a single-molecule electret with a functional memory. The results were published Oct. 12 in Nature Nanotechnology.
Along with colleagues at Nanjing University, Renmin University, Xiamen University, and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Mark Reed, the Harold Hodgkinson Professor of Electrical Engineering & Applied Physics demonstrated a single-molecule electret with a functional memory. The results were published Oct. 12 in Nature Nanotechnology.