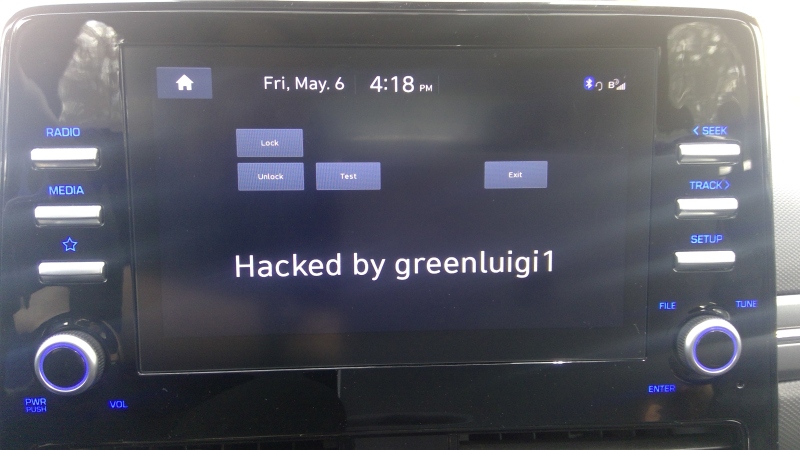
[greenluigi1] bought a Hyundai Ioniq car, and then, to our astonishment, absolutely demolished the Linux-based head unit firmware. By that, we mean that he bypassed all of the firmware update authentication mechanisms, reverse-engineered the firmware updates, and created subversive update files that gave him a root shell on his own unit. Then, he reverse-engineered the app framework running the dash and created his own app. Not just for show – after hooking into the APIs available to the dash and accessible through header files, he was able to monitor car state from his app, and even lock/unlock doors. In the end, the dash got completely conquered – and he even wrote a tutorial showing how anyone can compile their own apps for the Hyundai Ionic D-Audio 2V dash.
In this series of write-ups [greenluigi1] put together for us, he walks us through the entire hacking process — and they’re a real treat to read. He covers a wide variety of things: breaking encryption of .zip files, reprogramming efused MAC addresses on USB-Ethernet dongles, locating keys for encrypted firmware files, carefully placing backdoors into a Linux system, fighting cryptic C++ compilation errors and flag combinations while cross-compiling the software for the head unit, making plugins for proprietary undocumented frameworks; and many other reverse-engineering aspects that we will encounter when domesticating consumer hardware.
This marks a hacker’s victory over yet another computer in our life that we aren’t meant to modify, and a meticulously documented victory at that — helping each one of us fight back against “unmodifiable” gadgets like these. After reading these tutorials, you’ll leave with a good few new techniques under your belt. We’ve covered head units hacks like these before, for instance, for Subaru and Nissan, and each time it was a journey to behold.
Source: Hacker Liberates Hyundai Head Unit, Writes Custom Apps | Hackaday