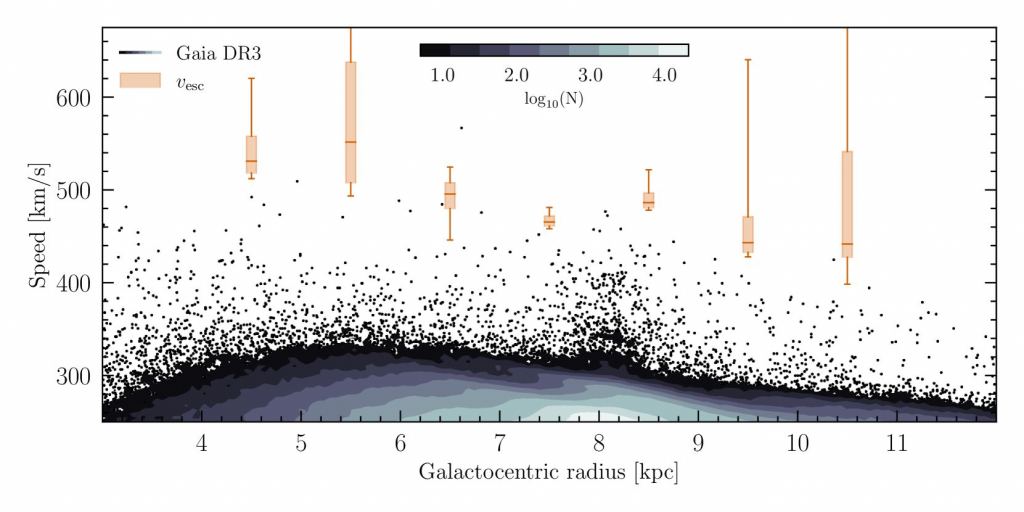
Dutch authorities are lifting the curtain on an attempted cyberattack last year at its Ministry of Defense (MoD), blaming Chinese state-sponsored attackers for the espionage-focused intrusion.
Specialists from the Netherlands’ Military Intelligence and Security Service (MIVD) and the General Intelligence and Security Service (AIVD) were called in to investigate an intrusion at an MOD network last year, uncovering a previously unseen malware they’re calling Coathanger.
The name, authorities said, was conjured up based on the “peculiar phrase” displayed by the malware when encrypting the configuration on disk: “She took his coat and hung it up.”
A deep dive into Coathanger’s code revealed the remote access trojan (RAT) was purpose-built for Fortinet’s FortiGate next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) and the initial access to the MoD’s network was gained through exploiting CVE-2022-42475.
According to the MIVD and AIVD, the RAT operates outside of traditional detection measures and acts as a second-stage malware, mainly to establish persistent access for attackers, surviving reboots and firmware upgrades.
Even fully patched FortiGate devices could still have Coathanger installed if they were compromised before upgrading.
In the cybersecurity advisory published today, authorities said the malware was highly stealthy and difficult to detect using default FortiGate CLI commands, since Coathanger hooks most system calls that could identify it as malicious.
They also made clear that Coathanger is definitely different from BOLDMOVE, another RAT targeting FortiGate appliances.
“For the first time, the MIVD has chosen to make public a technical report on the working methods of Chinese hackers. It is important to attribute such espionage activities by China,” said defense minister Kajsa Ollongren in an automatically translated statement. “In this way, we increase international resilience against this type of cyber espionage.”
The advisory also noted that Dutch authorities had previously spotted Coathanger present on other victims’ networks too, prior to the incident at the MOD.
As for attribution, MIVD and AIVD said they can pin Coathanger to Chinese state-sponsored attackers with “high confidence.”
“MIVD and AIVD emphasize that this incident does not stand on its own, but is part of a wider trend of Chinese political espionage against the Netherlands and its allies,” the advisory reads.
The attackers responsible for the attack were known for conducting “wide and opportunistic” scans for exposed FortiGate appliances vulnerable to CVE-2022-42475 and then exploiting it using an obfuscated connection.
After gaining an initial foothold inside the network, which was used by the MOD’s research and development division, the attackers performed reconnaissance and stole a list of user accounts from the Active Directory server.
Not much else was said about the attacker’s activity, other than the fact that the overall impact of the intrusion was limited thanks to the MOD’s network segmentation.
For those worried about whether Chinese cyberspies are lurking in their firewall, the Joint Signal Cyber Unit of the Netherlands (JCSU-NL) published a full list of indicators of compromise (IOCs) and various detection methods on its GitHub page.
The collection of materials includes YARA rules, a JA3 hash, CLI commands, file checksums, and more. The authorities said each detection method should be seen as independent and used together since some focus on general IOCs and others were developed to spot Coathanger activity specifically.
If there is evidence of compromise, it’s possible other hosts that are reachable by the FortiGate device are also compromised. There is also an increased likelihood that attackers may perform hands-on-keyboard attacks.
Affected users should isolate their device immediately, collect and review logs, and consider calling in third-party digital forensics specialists, the advisory reads. Victims should also inform their country’s cybersecurity authority: NCSC, CISA, etc.
The only way to remove Coathanger from an infected device is to completely reformat the device, before reinstalling and reconfiguring it.
Whiffs of China’s involvement in CVE-2022-42475 exploits have long been suspected, but for the first time they’re confirmed today.
First disclosed in December 2022, a month later Fortinet said it was aware that the vulnerability was tied to the breach of a government or government-related organization that had been infected with custom-made malware.
At the time, no fingers were officially pointed other than the fact that this custom malware was compiled on a machine in the UTC+8 timezone, so realistically it was most likely going to be either China or Russia.
China was also accused of being behind exploits of separate Fortinet bug in March, again using bespoke malware for the purposes of cyber espionage. ®