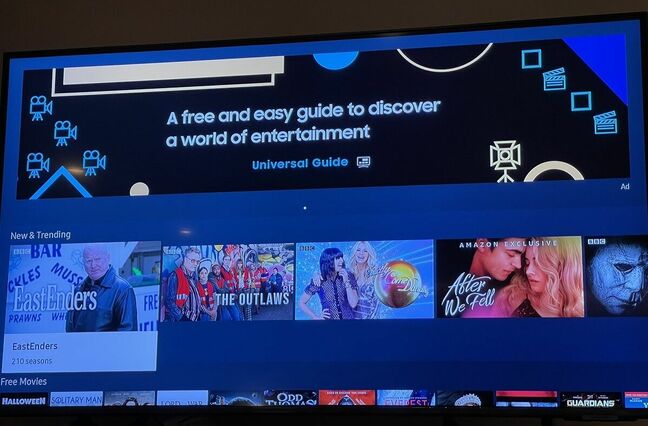
A Register reader triggered a kerfuffle for Samsung after asking the electronics biz if he could disable large and intrusive adverts splattered across his new smart TV’s programme guide.
Ross McKillop bought the telly from UK retailer John Lewis but felt distinctly undersold when he turned it on to find the internet-connected device displaying advertising on its electronic programme guide menu.
“If you press the menu button to change between like TV or Netflix or, or whatever, even different sources, there’s an advert panel,” lamented McKillop to The Reg. “It seems that people accept this.”
Irritated by the giant advert for Samsung’s own wares, McKillop took to Twitter to ask the obvious question. The answer was surprisingly blunt.
Hey, Ross. Congratulations on your new TV. You wouldn’t be able to disable the ads we’re afraid. ^HA
— Samsung UK (@SamsungUK) October 27, 2021
“The more annoying [advert],” McKillop told us, “is the one that appears on the application menu, on every menu [level].”
Such a problem is, sadly, not new, as we reported about a year ago when other Samsung TV customers began wondering where the giant adverts splattered all over their TVs’ user interfaces had come from.
“I expect Netflix to promote Netflix’s products or Netflix programming on a service I pay for because it’s a service,” stormed McKillop, adding that he didn’t expect to have his TV’s manufacturer insert unavoidable advertising into his new box.
Smart readers (like our man Ross) know that you can kill ads at home with innovations such as the Pi-Hole home network-level adblocker.
Our reader also pointed out that the adverts on his new internet-connected telly were not visible in Samsung’s marketing videos about the product.
We asked Samsung if it wished to comment. The manufacturer failed to respond. McKillop has since returned his TV to retailer John Lewis.
Samsung has been relatively open about what its smart TVs do. A quick look at the “Samsung privacy policy – smart TV supplement” on its UK website reveals that the company hoovers up information about “your TV viewing history” including “information about the networks, channels, websites visited, and programs viewed on your Samsung Smart TV and the amount of time spent viewing them”.
This kind of subtle-but-invasive monitoring was the subject of a warning by an American university professor in 2019 who described it as “a cesspit of surveillance”.
The devices can pose a security risk unless they’re treated like any other internet-connectable device, as the Korean giant itself reminded tellywatchers a couple of years ago (well, they deleted that Twitter missive but El Reg doesn’t forget).
All in all, if you’re buying a Samsung TV, just remember that you’re not only paying for a big panel so you can watch reruns of Friends; you’re also paying to be part of Samsung’s global TV advertising network.
Source: Reg reader ditches Samsung smart TV after seeing huge UI ads • The Register