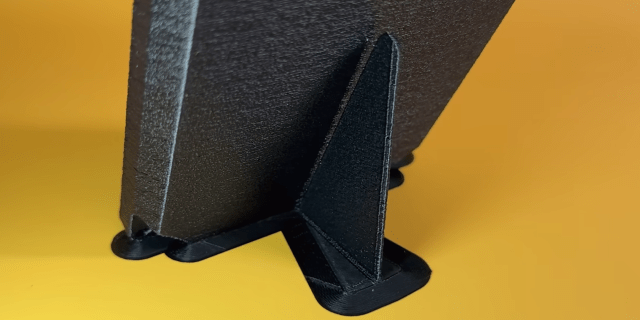
When it comes to 3D printing, the orientation of your print can have a significant impact on strength, aesthetics, and functionality or ease of printing. The folks at Slant 3D have found that printing enclosures at a 45° provides an excellent balance of these properties, with some added advantages for high volume printing. The trick is to prevent the part from falling over when balance on a edge, but in the video after the break [Gabe Bentz] demonstrate Slant 3D’s solution of minimalist custom supports.
The traditional vertical or horizontal orientations come with drawbacks like excessive post-processing and weak layer alignment. Printing at 45° reduces waste and strengthens the end product by aligning the layer lines in a way that resists splitting across common stress points. When scaling up production, this orientation comes with the added advantage of minimal bed contact area, allowing the printer to auto-eject the part by pushing it off the bed with print head.
To keep the part stable while printing in this orientation Slant 3D designed a fin-like support structure attached to the back of the enclosure with small sprues. This wastes significantly less time and material than auto-generated supports, and snaps away cleanly, leaving behind minimal imperfections that are easily addressed. To improve aesthetics and hide layer lines, Slant 3D also recommend adding texture to the external surfaces of enclosures. On 3D printed parts this detail costs nothing, while it would have added significant costs to injection molded parts.
We’re intrigued by this creative twist on 3D printing’s capabilities—proving once again that a simple shift in perspective (or in this case, orientation) can unlock new design potentials.
Slant 3D use FDM 3D printing for mass production [Gabe] even hosted a Hack Chat on the subject. They have come up with a number of innovative design tricks which are also useful for the hobbyist. These include improved corner brackets, robust living hinges and better alignment features for 3d printed assemblies.
Source: An Alternative Orientation For 3D Printed Enclosures | Hackaday