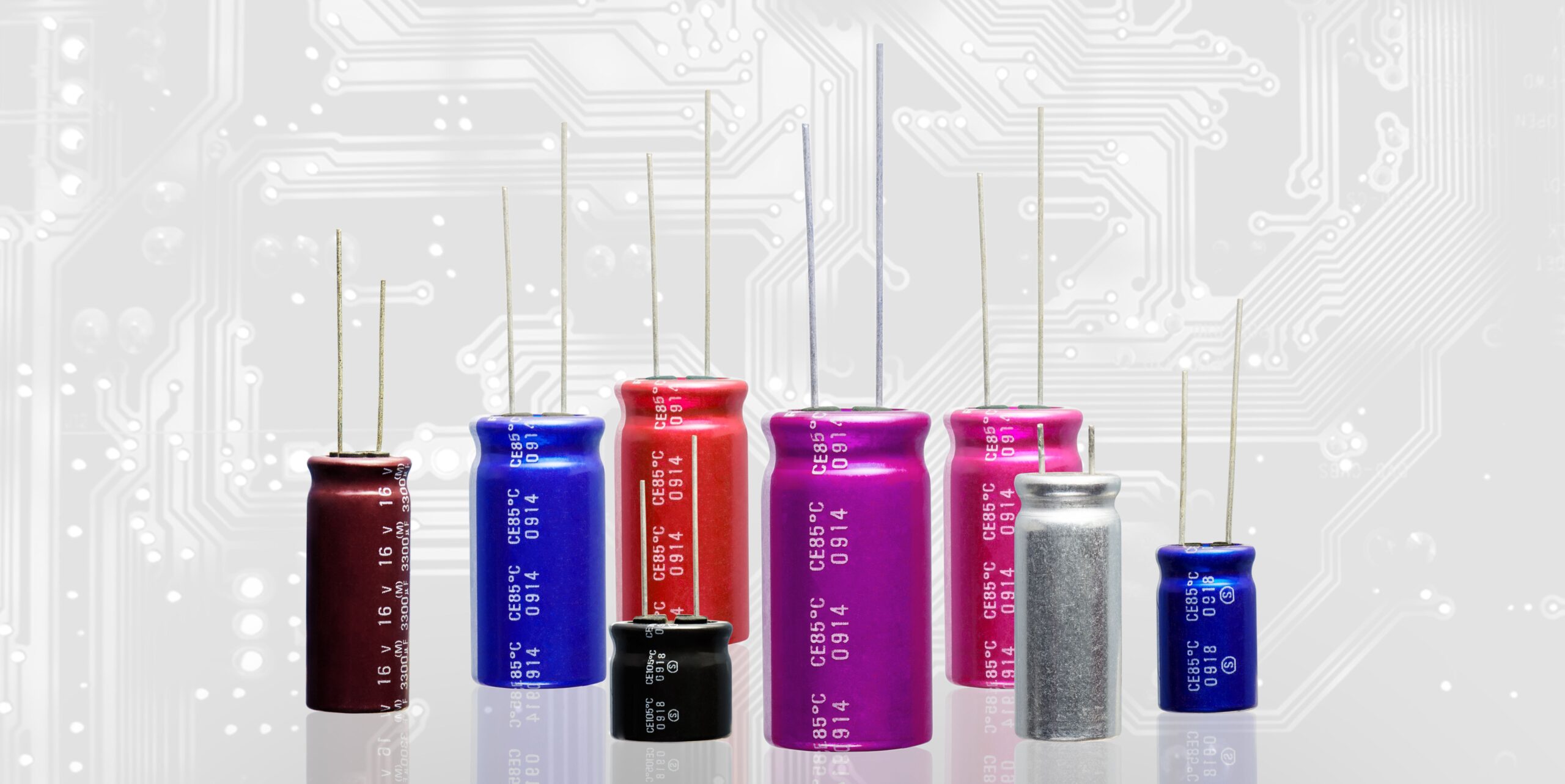
A battery’s best friend is a capacitor. Powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, capacitors store energy from a battery in the form of an electrical charge and enable ultrafast charging and discharging. However, their Achilles’ heel has always been their limited energy storage efficiency.
Now, Washington University in St. Louis researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking capacitor design that looks like it could overcome those energy storage challenges.
In a study published in Science, lead author Sang-Hoon Bae, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering and materials science, demonstrates a novel heterostructure that curbs energy loss, enabling capacitors to store more energy and charge rapidly without sacrificing durability.
While batteries excel in storage capacity, they fall short in speed, unable to charge or discharge rapidly. Capacitors fill this gap, delivering the quick energy bursts that power-intensive devices demand. Some smartphones, for example, contain up to 500 capacitors, and laptops around 800. Just don’t ask the capacitor to store its energy too long.
Within capacitors, ferroelectric materials offer high maximum polarization. That’s useful for ultra-fast charging and discharging, but it can limit the effectiveness of energy storage or the “relaxation time” of a conductor.
[…]
Bae makes the change—one he unearthed while working on something completely different—by sandwiching 2D and 3D materials in atomically thin layers, using chemical and nonchemical bonds between each layer. He says a thin 3D core inserts between two outer 2D layers to produce a stack that’s only 30 nanometers thick
[…]
“Initially, we weren’t focused on energy storage, but during our exploration of material properties, we found a new physical phenomenon that we realized could be applied to energy storage,” Bae says in a statement
[…]
The sandwich structure isn’t quite fully conductive or nonconductive. This semiconducting material, then, allows the energy storage, with a density up to 19 times higher than commercially available ferroelectric capacitors, while still achieving 90 percent efficiency—also better than what’s currently available.
The capacitor can hang on to its energy thanks to the minuscule gap in the material structure.
[…]
The study team will continue to optimize the material structure to ensure ultrafast charging and discharging with a new high-energy density. “We must be able to do that without losing storage capacity over repeated charges,” Bae says, “to see this material used broadly in large electronic like electric vehicles.”
Source: Capacitor Breakthrough: 19-Fold Increase in Energy Storage Potential