The CheapAir.com 2019 Annual Airfare Study is based on an analysis of 917 million airfares in more than 8,000 markets. Following the recommendations could save you hundreds of dollars on your travel this year.
This report will break down:
- The average “best day” to buy your airline ticket
- The airfare booking “zones” – what you can expect to pay for an airfare depending on when you buy
- How to identify the Prime Booking Window™ – the range of dates you’ll be most likely to find a low price
- The best and worst days of the week to fly based on price
- How seasonality affects the price of your airline ticket
As you can see, this is a ton of information. But don’t worry. We’re going to break it down in digestible and easy-to-understand bites.
We’ve already done the research and we’re serving it up free. Before you know it, you’ll be buying those flights with understanding and confidence!
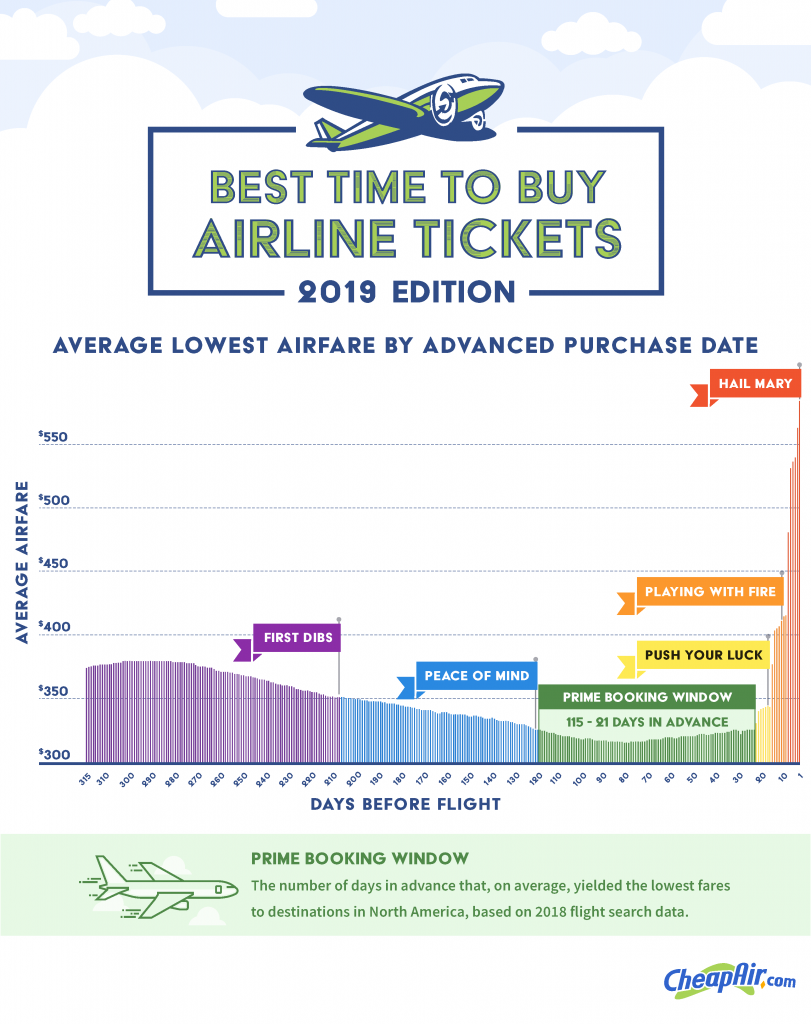
For 2018, the “best day to buy a flight” domestically (within the continental U.S.) was 76 days out from your travel date. That’s slightly higher than it was in last year’s report (70 days). Let’s take a bit of a deep dive into the different “booking zones” as airfares fall and rise. Each zone has benefits and risks.
The 6 Airfare Booking Zones
We came up with booking zones to easily chart what an airfare looks like from the approximate time it is published about 11 months out, all the way up to the very last minute you can buy your ticket. Over the years we refined these zones to reflect the subtle differences between each. And we think this system is solid for showing you what you pay (depending on when you buy). Let’s dig in.

First Dibs
315 to 203 Days in Advance
(about 10 months to 6.5 months)
We like to recommend First Dibs for buyers with an agenda. You know who you are. You’re less motivated by price and more motivated by your flight preferences (such as a certain flight time or seat) and you want to lock in plans well in advance. Flights in the First Dibs zone do cost about $50 more per ticket than flights in the Prime Booking Window (the most affordable zone), on average. If you like to have many options, however, there’s no better time to buy.
Peace of Mind
202 to 116 Days in Advance
(about 6.5 to 4 months)
Peace of Mind is where you might want to land if you’ve got anxiety surrounding big airfare purchases coupled with FOMO for a good deal. When you’re in the Peace of Mind zone, you’ll likely pay just about $20 more than flights in the Prime Booking Window and you’re still buying early enough to have a decent amount of choice.
Prime Booking Window
115 to 21 Days in Advance
(about 4 months to 3 weeks)
This is where the magic happens, travelers. And while some of the other zones have shifted slightly from one year to the next, the Prime Booking Window stays pretty solid. What does this mean? Well, the data shows that the lowest airfares tend to pop up about 4 months to 3 weeks in advance of your travel dates. Fares in this zone are within 5% of their lowest point. Bargain shopping? Stay in the sweet spot – the Prime Booking Window.
Push Your Luck
20 to 14 Days in Advance
(3 – 2 weeks)
We’re heading into gambling territory once you get within 2-3 weeks of your travel dates. The odds of getting a “cheap ticket” start to decrease heading into the Push Your Luck zone, though if you do like to roll the dice you may still find cheap tickets. One important factor to consider – though there could be lower priced fares in Push Your Luck, the quantity and quality of seats is more limited the closer we get to the travel date. You may find yourself paying slightly more for a subpar seat.
Playing with Fire
13 to 7 Days in Advance
(2 – 1 weeks)
No matter how long we’re in the airfare prediction game, we find that some people just like to play with fire. Hence, we carved out the Playing with Fire zone. You’ll almost always pay more than Prime Booking Window buyers, but pay less (close to $135, on average) than people who wait until the very last minute to buy. In this zone, choice is even more limited.
Hail Mary
6 to 0 Days in Advance
(less than a week)
How did we get here? Usually, people who are buying in the Hail Mary zone are doing so because of an unexpected trip, not because waiting until less than a week from your travel date was a conscious choice. You’re going to have to cope with the least amount of choice in the Hail Mary zone, and you’re apt to pay almost $220 more than you would have if this ticket was purchased in the Prime Booking Window.
Hawaii as Outlier
Our 50th state is a bit of a standalone. We do not include Hawaii in our main airfare data for a couple of reasons. Hawaii’s distance from the mainland in conjunction with its unique characteristic as a leisure destination means that is has a different dynamic. Check out our separate post on Buying Flights to Hawaii for the best tips and strategies for snagging a low fare to the islands.
There are other factors to consider aside from when you buy that will affect your travel budget. Let’s look at days of the week, for example.
Do Days of the Week Have an Effect on Price?
We can start by dispelling one myth. What day of week you purchase a flight has a negligible effect on flight cost. The average low fare only varies by $1 based on the purchase day of week. Whether you buy that ticket on Tuesday or Sunday it’s going to cost about the same.
On the other hand, there are definitely less expensive days and more expensive days to fly. Tuesday is the cheapest day of the week to fly, nearly $85 cheaper on average than the most expensive day of the week to travel, Sunday. Wednesdays are also great days for air travel. Friday is the second most expensive day of the week to fly. A good rule of thumb – weekends are more expensive and midweek flights save travelers cash.
Don’t Underestimate Seasonality
What time of year you travel can also have an impact on your flight cost. We broke down the seasons and included the most popular time frames in each, to offer travelers an easy reference for finding the best fares. This simple chart tells the story:

When to Buy Winter Flights
If you can avoid Christmas week and ski destinations, most winter destinations offer good value for the money.
- The average best time to buy is 94 days from travel (just over 3 months)
- The prime booking window is 74 to 116 days (about 2.5 months to nearly 4 months)
- The average domestic fare for winter travel is $433, by far the most expensive time of the year for air travel
- The difference between the best and worst priced days is $168, which is quite a bit lower than in other seasons. There is much less volatility in airfare pricing all season.
When to Buy Spring Flights
Plan ahead for spring flights. There are no major travel holidays in the spring, but both families and college students enjoy spring break for much of March and April. Take advantage of lower mid-week prices to help keep costs down.
- The average best time to buy is 84 days from travel, or nearly 3 months
- The prime booking window is 47 to 119 days (about 1.5 months to just under 4 months)
- The average domestic fare for spring travel is $354
- The difference between the best and worst priced days is $285
When to Buy Summer Flights
Americans travel a ton in the summer, and the peak summer dates of June 15 – August 15 are when the bulk of travel happens. You can find the best deals the closer you get to the end of the season (late August and September will give you the best odds to score low airfare.
- The average best time to buy is 99 days out from travel
- The prime booking window is 21 to 150 days (about 3 weeks to 5 months)
- The average domestic fare for peak summer travel is $365
- The difference between the best and worst priced days is $260
- Late summer and early fall is shoulder season, and as such, offers great deals (Labor Day weekend notwithstanding). Flying the second half of August on into September is the sweet spot for these deals.
When to Buy Fall Flights
Overall, fall offers great value for budget travelers. Fall is shoulder season for a lot of destinations, and people simply do not travel as much. Of course, the one exception to this rule is Thanksgiving week. Traveling during Thanksgiving? Better buy on the early side.
- The average best time to buy is 69 days from travel
- The prime booking window is 20 to 109 days (about 3 weeks to 3.5 months)
- The average domestic fare for fall travel is $342, which makes it the best season to find travel bargains
- The difference between the best and worst priced days is $280
Takeaways
Airfares change all the time. Don’t get bogged down in watching the tiny, incremental fluctuations. We recommend buying an airline ticket when you see a good fare and not hesitating or waffling. Since fares change a lot, when shoppers go away to think about it “for a while,” they’re often disappointed when they come back to find that the good fare has disappeared. Be prepared to buy.
Bookmark this page or commit the Prime Booking Window to memory. It’s where you should focus the bulk of your shopping efforts. Keep in mind that there is still volatility within the prime booking window. Though you can expect peaks and valleys in price, the best fares on average will be found here.
Also, keep in mind that CheapAir.com will “protect” your purchase with Price Drop Payback. Should your fare drop after you buy, we’ll reimburse you up to $100 per ticket.
Need advice for your next vacation abroad? Check back soon for our International When to Buy study results.
Happy Travels!