Neuroscientists and materials scientists have created contact lenses that enable infrared vision in both humans and mice by converting infrared light into visible light. Unlike infrared night vision goggles, the contact lenses, described in the journal Cell, do not require a power source—and they enable the wearer to perceive multiple infrared wavelengths. Because they’re transparent, users can see both infrared and visible light simultaneously, though infrared vision was enhanced when participants had their eyes closed.
“Our research opens up the potential for noninvasive wearable devices to give people super-vision,” says senior author Tian Xue, a neuroscientist at the University of Science and Technology of China. “There are many potential applications right away for this material. For example, flickering infrared light could be used to transmit information in security, rescue, encryption or anti-counterfeiting settings.”
The contact lens technology uses nanoparticles that absorb infrared light and convert it into wavelengths that are visible to mammalian eyes (e.g., electromagnetic radiation in the 400–700 nm range). The nanoparticles specifically enable the detection of “near-infrared light,” which is infrared light in the 800–1600 nm range, just beyond what humans can already see.
The team previously showed that these nanoparticles enable infrared vision in mice when injected into the retina, but they wanted to design a less invasive option.
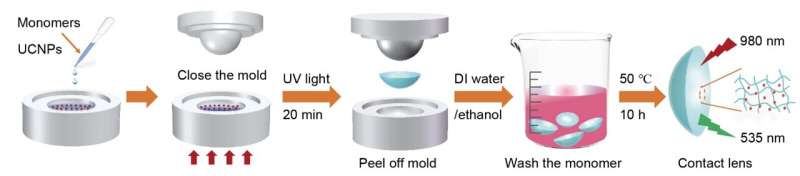
To create the contact lenses, the team combined the nanoparticles with flexible, nontoxic polymers that are used in standard soft contact lenses. After showing that the contact lenses were nontoxic, they tested their function in both humans and mice.
Preparation procedures for infrared contacts. Credit: Sheng Wang
[…]
In humans, the infrared contact lenses enabled participants to accurately detect flashing morse code-like signals and to perceive the direction of incoming infrared light.
“It’s totally clear-cut: without the contact lenses, the subject cannot see anything, but when they put them on, they can clearly see the flickering of the infrared light,” said Xue.
“We also found that when the subject closes their eyes, they’re even better able to receive this flickering information, because near-infrared light penetrates the eyelid more effectively than visible light, so there is less interference from visible light.”
An additional tweak to the contact lenses allows users to differentiate between different spectra of infrared light by engineering the nanoparticles to color-code different infrared wavelengths. For example, infrared wavelengths of 980 nm were converted to blue light, wavelengths of 808 nm were converted to green light, and wavelengths of 1,532 nm were converted to red light.
In addition to enabling wearers to perceive more detail within the infrared spectrum, these color-coding nanoparticles could be modified to help color-blind people see wavelengths that they would otherwise be unable to detect.
“By converting red visible light into something like green visible light, this technology could make the invisible visible for color-blind people,” says Xue.
Because the contact lenses have limited ability to capture fine details (due to their close proximity to the retina, which causes the converted light particles to scatter), the team also developed a wearable glass system using the same nanoparticle technology, which enabled participants to perceive higher-resolution infrared information.
Currently, the contact lenses are only able to detect infrared radiation projected from an LED light source, but the researchers are working to increase the nanoparticles’ sensitivity so that they can detect lower levels of infrared light.
“In the future, by working together with materials scientists and optical experts, we hope to make a contact lens with more precise spatial resolution and higher sensitivity,” says Xue.
More information: Near-Infrared Spatiotemporal Color Vision in Humans Enabled by Upconversion Contact Lenses, Cell (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.04.019. www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(25)00454-4
[…]”Spectrometers are critical tools for helping us understand the chemical and physical properties of various materials based on how light changes when it interacts with those materials,” says Brendan O’Connor, corresponding author of a paper on the work and a professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at North Carolina State University. “They are used in applications that range from manufacturing to biomedical diagnostics. However, the smallest spectrometers on the market are still fairly bulky.












 Spotify’s brief attempt at being a hardware company wasn’t all that successful: the company
Spotify’s brief attempt at being a hardware company wasn’t all that successful: the company