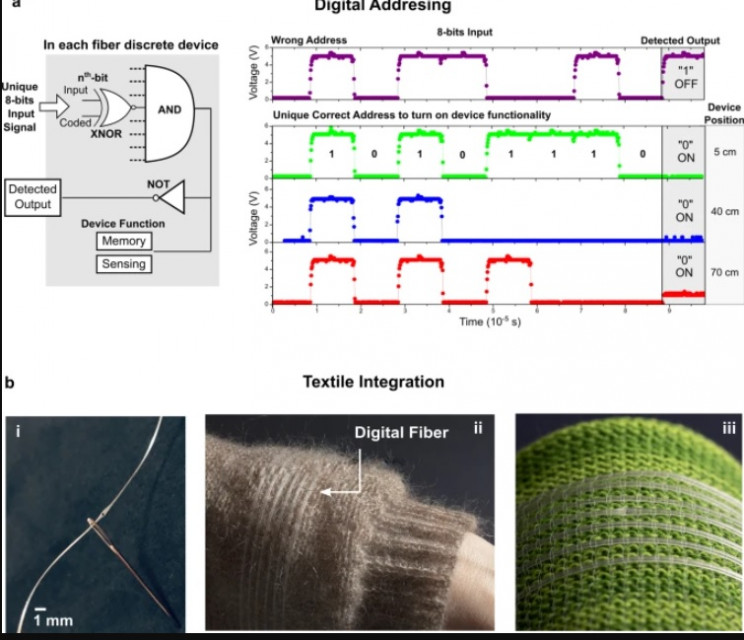
The FBI has revealed how it managed to hoodwink the criminal underworld with its secretly backdoored AN0M encrypted chat app, leading to hundreds of arrests, the seizure of 32 tons of drugs, 250 firearms, 55 luxury cars, more than $148M, and even cocaine-filled pineapples.
About 12,000 smartphones with AN0M installed were sold into organized crime rings: the devices were touted as pure encrypted messaging tools — no GPS, email or web browsing, and certainly no voice calls, cameras, and microphones. They were “designed by criminals, for criminals exclusively,” one defendant told investigators, Randy Grossman, Acting US Attorney for the Southern District of California, told a press conference on Tuesday.
However, AN0M was forged in a joint operation by Australian and US federal law enforcement, and was deliberately and surreptitiously engineered so that agents could peer into the encrypted conversations and read crooks’ messages. After Australia’s police broke the news that the messaging app had recorded everything from drug deals to murder plots — leading to hundreds of arrests — now the FBI has spilled its side of the story, revealing a complex sting dubbed Operation Trojan Shield.

The Dept of Justice’s Randy Grossman walks through journalists through Operation Trojan Shield at a press conference on Tuesday
“For the first time the FBI developed and operated its own hardened encrypted device company, called AN0M,” Grossman said.
“Criminal organizations and the individual defendants we have charged purchased and distributed AN0M devices in an effort to secretly plan and execute their crimes. But the devices were actually operated by the FBI.”
Playing the long game
According to court documents [PDF] this all came about after the shutdown of Phantom Secure, a Canadian biz selling Blackberry phones customized for encrypted chat to the criminal community. CEO Vincent Ramos pleaded guilty in 2018 to conspiring with drug traffickers and was sentenced to nine years behind bars and had $80M in assets seized.
The closure of Phantom Secure put the staff working there on the FBI’s radar. The bureau’s San Diego office recruited a developer at the company as a confidential human source (CHS), court documents state. This source had previously been sentenced to six years in the clink for importing illegal drugs, and agreed to cooperate with the Feds to reduce any future punishment potentially coming their way.
Crucially, not only had this programmer worked on the Phantom Secure’s encrypted messaging software, but they were also doing work on rival encrypted comms service Sky Global — which also sold modified handsets with secure messaging features — as well as developing their own secure customized phone called AN0M.
“The CHS … had invested a substantial amount of money into the development of a new hardened encrypted device,” the indictment by FBI Special Agent Nicholas Cheviron reads.
“The CHS offered this next generation device, named ‘AN0M,’ to the FBI to use in ongoing and new investigations. The CHS also agreed to offer to distribute AN0M devices to some of the CHS’s existing network of distributors of encrypted communications devices.”
And so, in October 2018, the three-year sting operation began.
The CHS — who was paid $120,000 plus $59,000 in living and travel expenses by the authorities — worked with the FBI and the Australian Federal Police to hide a master decryption key into the AN0M app. Messages sent by the software’s users were quietly copied and sent off to servers controlled by law enforcement, who were able to use the key to decrypt the texts.
[…]
In this beta test, 50 handsets were passed out Down Under, and this phase of the operation was successful; two of the country’s biggest criminal gangs were successfully penetrated and the message copying system worked perfectly. Aussie police reviewing the texts said they found 100 per cent were related to crime. Everyone who used the app was assigned a unique ID, and these handles were known to the police.
Let’s go global
In the next phase, the CHS expanded the distribution network beyond Australia, and the FBI found itself in a position to collect the data. After negotiations with an unnamed third country, a message-relaying iBot server was set up in that nation to collect the BCC’d conversations, and on October 21, 2019, it began beaming copies of crooks’ chats from AN0M handhelds to an FBI-owned system every Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. The third country’s officials had secured a court order for the surveillance, and the FBI used a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty, also known as an MLAT, to obtain the decrypted material.
Sales of AN0M grew steadily, and got a boost when French and Dutch police took down the EncroChat encrypted service in 2020. When a similar swoop shuttered Sky Global in 2021, demand skyrocketed. After the latter take-down, AN0M sales tripled to more than 9000 handsets, each costing $1700 with a six-month subscription to the AN0M encrypted messaging network, Grossman said.
The data haul from the application was immense: more than 27 million messages from 100 countries, and between 300 criminal gangs. This included more than 400,000 photos, typically of drugs or guns and, crucially, shipment plans.
[…]
Police around the world have made 800 arrests from AN0M-gathered intelligence, including cuffing six US law enforcement officers. Of all of those detained, they primarily face charges of drug trafficking, money laundering, gun violations, and violent crime.
Grossman also announced Uncle Sam had indicted 17 suspects on RICO charges relating to the use and marketing of the AN0M handsets. Most of these people are said to be distributors, though the prosecutor said three were administrators who helped run the service. Eight of those RICO suspects have already been collared and detained.
[…]