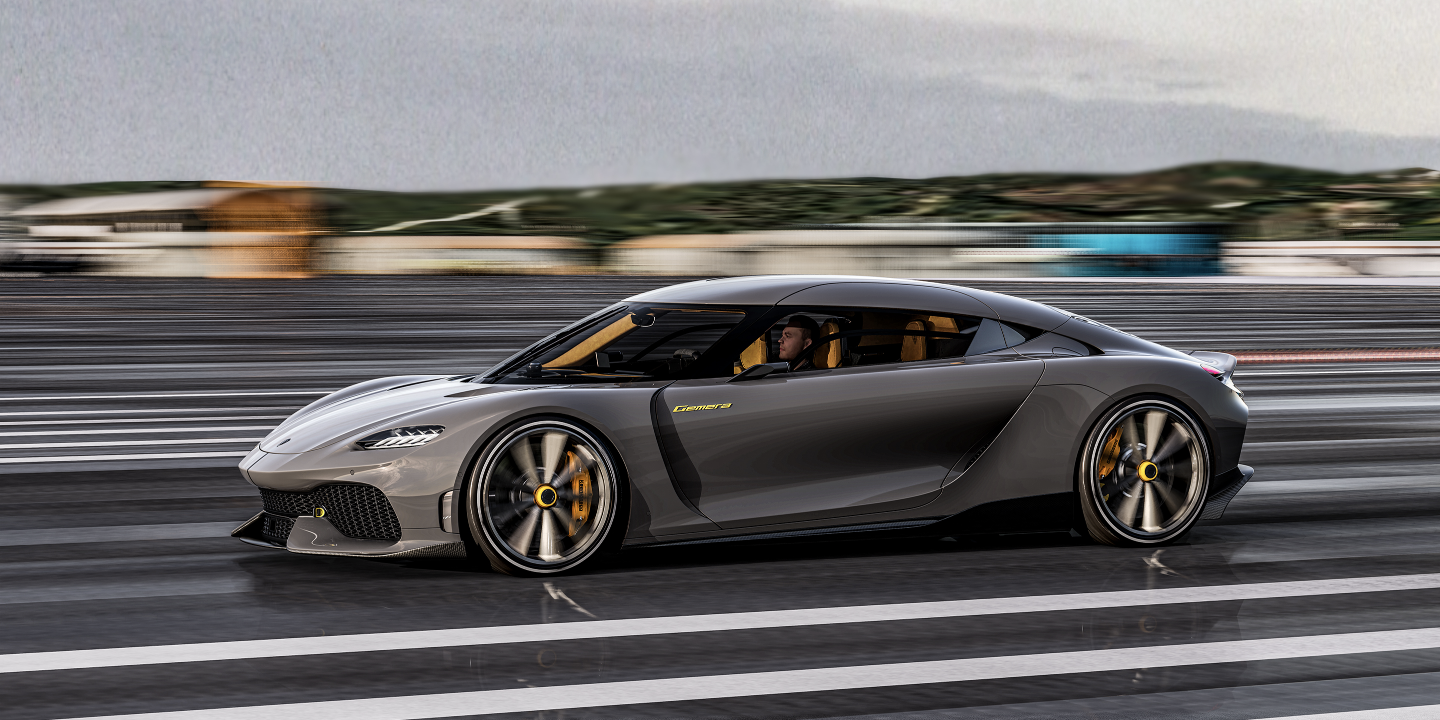
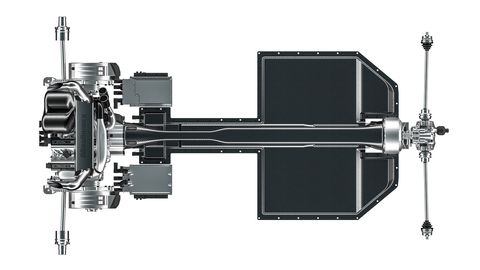
You can always count on Koenigsegg to do things differently. Take the Swedish brand’s newest car, the Gemera, a 1700-hp four-seat hybrid grand tourer that can crest 250 mph. In a world filled with more ultra-high-dollar supercars than ever, the Gemera stands out. And perhaps the most interesting thing about the car is its engine.
Koenigegg Gemera: 1700-HP Hybrid Four-Seater
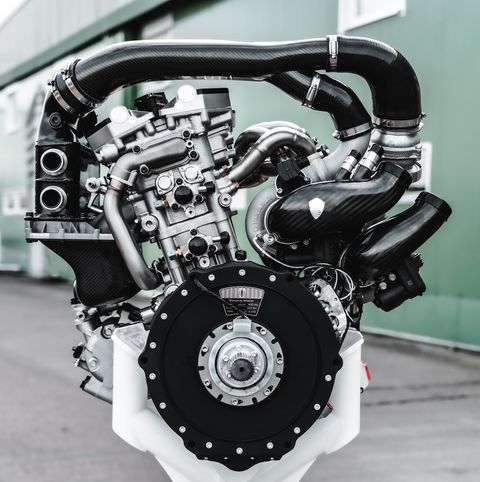
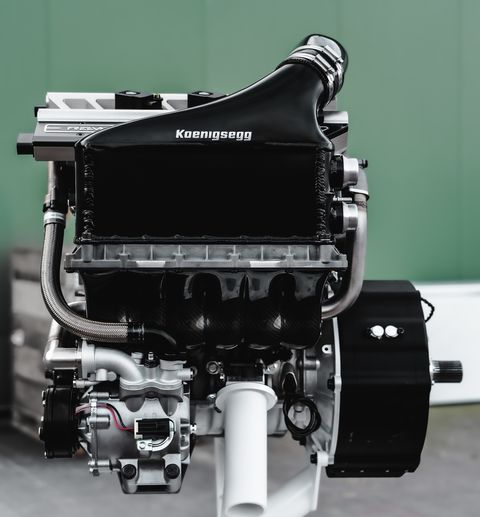
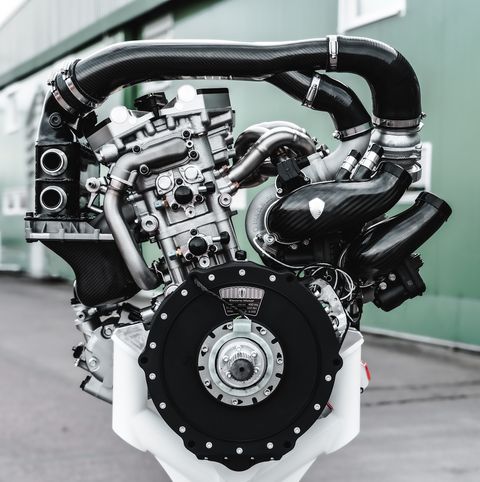
Koenigsegg calls the engine the Tiny Friendly Giant, or TFG for short, and it’s an apt name. The TFG is a 2.0-liter twin-turbo three-cylinder that makes 600 horsepower. At 300 horsepower per liter, the TFG’s specific output is far higher than anything ever seen in a road car. Koenigsegg says this is “light-years ahead of any other production three-cylinder today,” and he’s not wrong: The next most powerful triple is the 268-hp engine in the Toyota GR Yaris.
What’s even more unusual is that the TFG doesn’t have a camshaft. Instead, the engine uses technology from Koenigsegg’s sister company, Freevalve, with pneumatic actuators opening and closing each valve independently. I called company founder Christian von Koenigsegg to learn exactly how this unconventional engine works.
The Tiny Friendly Giant was designed specifically for the Gemera. Koenigsegg wanted something compact and lightweight, with big horsepower. Koenigsegg also decided to reverse the setup found in the hybrid Regera, where internal combustion provides the bulk of the total power output. In the Gemera, the majority of the power comes from electric motors, with the Gemera contributing some driving force as well as charging the hybrid drivetrain’s batteries.
Given this criteria, Koenigsegg arrived at a 2.0-liter, three-cylinder configuration. “We were kind of scratching our heads a little bit,” Koenigsegg says. “A three-cylinder is not the most exclusive… but then we realized, per cylinder, this is the most extreme engine on the planet, technically. And why should we have more than we need to make the car as lightweight as possible, as roomy as possible?”
The rest has to do with the engine’s character. “It’s a big-bore, big-stroke engine, and it doesn’t sound puny like some three-cylinders do,” Koenigsegg says. “Imagine a Harley with one more cylinder. That kind of sensation.” Despite the 95mm bore and 93.5mm stroke dimensions, the TFG is quite high-revving. Peak power comes at 7500 rpm and redline is set at 8500. “We have a tendency to engineer these rotating parts lighter than anyone else,” Koenigsegg explains, “but really focusing on strength at the same time. And if you do that, you can rev higher.” The tiny engine also delivers big torque—443 lb-ft from just below 3000 rpm all the way to 7000.
The sequential turbo setup is ingenious. The TFG has two exhaust valves per cylinder, one of which is dedicated to the small turbo, the other to the big turbo. At low revs, only the small-turbo exhaust valve opens, giving sharp boost response. Past 3000 rpm, the big-turbo exhaust valves start opening, building huge boost and lots of midrange power and torque. (Even without the turbos, the TFG is impressive: Koenigsegg says, in theory, a naturally aspirated TFG could make 280 horsepower.)
“It’s called Freevalve for a reason,” Koenigsegg says. “Each individual valve has total freedom. How much to open, when to open, how long to stay open.” At low loads, only one of the two intake valves per cylinder opens, distributing atomized fuel more evenly. With the Freevalve system constantly fine-tuning intake valve lift and duration, there’s no need for a conventional throttle, and the engine can shut down individual cylinders on the fly. Freevalve also allows the TFG to switch between traditional Otto cycle and Miller cycle operation, where intake valves are left open longer to help reduce pumping losses, increasing power and efficiency. And that’s not even the craziest thing. “With the help of the turbos, this engine can run two-stroke up to somewhere around 3000 rpm. It’ll sound like a straight-six at 6000 rpm,” Koenigsegg says. Beyond 3000 rpm, the TFG would have to switch back to four-stroke operation, because there’s not enough time for gas exchange at higher revs. This is just in theory, though—the company hasn’t tested the TFG in two-stroke mode yet. Koenigsegg says it’s still “early days.”
Koenigsegg is also working with a Texas artificial intelligence company, SparkCognition, to develop AI engine management software for Freevalve engines like the TFG. “The system will learn over time the best ways to operate the valves, what’s most frugal, what’s cleanest… It will eventually start doing things we’ve never thought of,” Koenigsegg says. “It’ll float in and out of different ways of combusting by itself, eventually in ways not completely understandable to us.” But that’s way out. Koengisegg says that the TFG will rely on human-coded valve operation for now.
The TFG makes “only” about 500 horsepower on regular pump gas. This is a flexible-fuel engine optimized to burn alcohol—ethanol, butanol, or methanol, or any combination thereof. Alcohol fuels are great for performance, but Koenigsegg says their use is also a key part of making the TFG clean, since they generate fewer harmful particulates than gasoline. And with sustainably-sourced fuel, the TFG can be effectively carbon-neutral.
Of course, a complex system like Freevalve is more expensive than a conventional cam setup—but Koenigsegg points out that the system uses less raw material, offsetting some of the cost and shaving weight from the engine. All in all, the TFG engine is about half as costly to build as Koenigsegg’s 5.0-liter twin-turbo V-8.
The rest of the Gemera drivetrain is equally unconventional. The TFG sits behind the passenger compartment, driving the front wheels through Koenigsegg’s outrageous direct-drive system, no gearbox necessary. When asked about the unusual mid-engine front-drive setup, Koenigsegg replies, “Why do many traditional cars have an engine in the front, a propshaft, and drive on the rear axle?” An electric motor/generator attached to the TFG’s crankshaft charges the hybrid drivetrain’s batteries and contributes up to 400 hp of additional power, while each rear wheel is driven by a 500-hp electric motor. Peak total output is 1700 hp.
“Koenigsegg cars are mid-engine cars,” the founder explains. “We don’t make pure electric cars because for the time being, we think they’re too heavy, and they don’t make a cool sound. And as long as we can be CO2 neutral and frugal and clean comparatively, we will push the combustion engine.”
The TFG is a technology showcase, an alternate vision for the automotive future. Koenigsegg posits that with some left-field thinking, the internal-combustion engine can still have a place in the electrified automotive world. “In my mind, it’s kind of the engine,” Koenigsegg says. “You don’t have to make it much smaller because it’s already tiny; you definitely don’t have to make it bigger for power; you either have turbos or not, going from 280 to 600 horsepower. And if that’s not enough, you put an electric motor on it, then you have a hybrid with [more than] 1000 horsepower.”
Koenigsegg once again has produced something remarkable with the Tiny Friendly Giant. And I think you’ll agree, the name is apt.